
Abstract: As one of country's most important driving forces for economic development, the real estate sector has been severely hit by the novel coronavirus outbreak. A large number of real estate companies are facing difficulties in maintaining a healthy cash flow. In this case, governments at all levels should relax policy restrictions for the housing sector and prevent serious negative impacts of widespread bankruptcies of housing companies.
I. Commercial housing sales have stagnated
Affected by the novel coronavirus outbreak, the volume of commercial housing sales across the country has fallen sharply since the Spring Festival holiday (Jan 24-30). During the holiday, the transaction volume in 30 large and medium-sized cities decreased by 80.8% compared to last year's Spring Festival holiday period (Feb 4-10), and that in the week following the holiday declined by 97.3% compared to the same period last year. Even though people have gradually returned to work in most regions across the country, the transaction volume of commercial housing has remained at a very low level, which is in sharp contrast to the situations in previous years.
Figure 1: Commercial housing sales in 30 cities
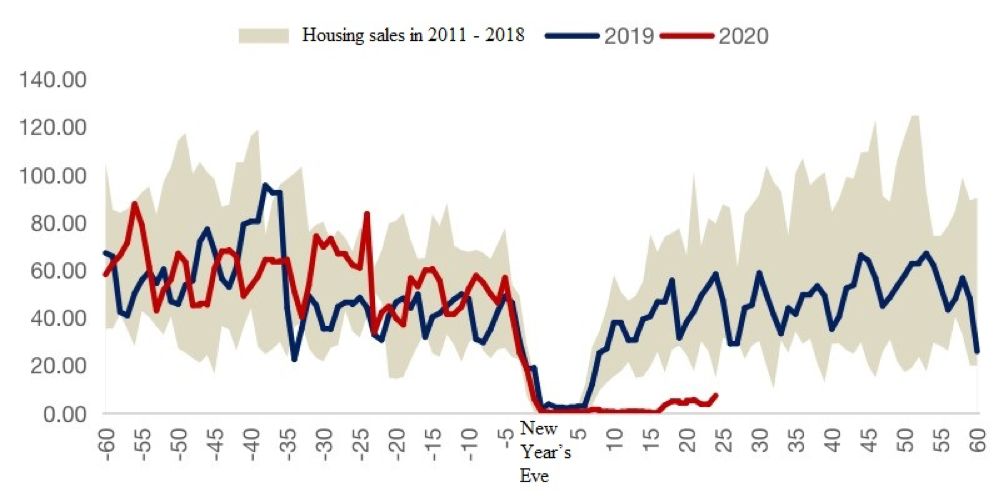
Source: Wind
From a short-term perspective, whether the sales of commercial housing can improve will largely depend on developments of the epidemic which still faces many uncertainties. The household sector can postpone house purchase plans for several months, while real estate companies will find their capital chains severely challenged. When companies are not able to sustain themselves, underselling may become a choice for some.
II. Real estate sector financing faces policy constraint
Regulation and control of the real estate sector have become stricter since 2017. Financing channels such as banks, trusts, and even overseas bond issuance have faced policy constraints. Against this background, financial institutions have been tightening credit supply for real estate companies. Policy direction is out of question from the perspective of deleveraging, preventing risks and stopping excessive capital and resources from flowing into real estate.
However, under the influence of the epidemic, most enterprises with financing needs have suspended their roadshows. At the regulatory level, approval of financing applications has slowed down. Real estate enterprises have consequently significantly reduced debt issuance. From January 25 to February 10, the scale of bonds issued by 95 representative real estate companies was about 7.05 billion yuan, which was a sharp drop of 86% compared to the corresponding period of the 2019 Spring Festival (Finance United Press, February 17). After February 10, real estate companies issued more short-term and even ultra-short-term bonds to temporarily ease funding pressure. Short-term financing is relatively costly. It will further increase the financial pressure on housing companies if the impact of the epidemic lingers.
The scale of overseas financing is restricted by policies, and the costs of policy restrictions have risen due to the epidemic. The "Notice on the Relevant Requirements for the Registration and Application of Real Estate Enterprises' Issuance of Foreign Debts" issued in July 2019 stipulates that real estate enterprises can only issue foreign debts to replace medium and long-term foreign debts that are to mature within a year, which means that housing companies will find it hard to have overseas debt issuance approved if they have no overseas debt due in a year. In addition, as the impact of the epidemic on sales has grown, overseas investors are also concerned about the solvency of real estate enterprises, which has increased overseas financing costs to a certain extent. The interest rate of debt issuance by housing enterprises generally rises by about 1 to 2 points (Finance United Press, February 17).
III. Real estate enterprises face huge pressure of debt repayment and financial costs
In 2020, housing companies at large face huge debt repayment pressure and financial costs. According to Moody's calculations, in the next 12 months starting on February 1, approximately US$51.3 billion (about 358.14 billion yuan) of domestic bonds and US$ 27.6 billion (about 192.68 billion yuan) of overseas bonds will mature or be available for buy-back. Therefore, the refinancing demand of housing enterprises will remain at a high level.
Housing companies' financial expenditures are also facing severe challenges. Daily expenses include operating costs (installment payment for land purchase, construction of pre-sale housing, etc.), as well as payment of wages, interest, and taxes. At present, cash and cash equivalents of A-share listed real estate companies can only support daily expenses for 3 months (Ping An Securities, February 5), while unlisted real estate companies may face greater funding pressure.
At present, production recovery across the country is generally postponed, rate of work resumption is still at a low level, and there are restrictions on migrant workers returning to cities. Even when migrant workers return to their working cities, they have to be put into quarantine for one to two weeks. Construction sites also face problems such as protective supply shortages, and potential construction suspension if a confirmed case found. The extension of the construction period and hidden uncertainties will cause higher financial costs to real estate companies.
IV. Recognizing the importance of the real estate sector amid the current restrictive policies
First, real estate sector is a strong driving force for the Chinese economy, which can also turn into a burden. Real estate investment is one of the three pillars of fixed asset investment. In 2019, the growth of real estate investment is especially thriving. On the one hand, the real estate industry is large. In 2019, the real estate industry's value added accounted for 7% of China's GDP, and the construction industry 7.2%. The total of the two accounted for 14.2%, occupying an important position in the country's economy. On the other hand, the real estate industry involves a long industrial chain and many related industries. If the upstream and downstream industries are considered, the impact of real estate sector on the economy will be even greater.
Second, the country's credit system and revenue of local governments are strongly dependent on real estate. Indirect financing dominates China's financial system, and real estate assets are the most important collateral, hence critical for credit expansion. If housing enterprises face capital chain pressure, they may have to ease the pressure through discount promotions, which will bring down housing prices, which in turn may threaten the stability of China's credit system.
At the same time, taxes and fees collected from the real estate industry are an important source of income for some local governments. First, real estate-related taxes are an important revenue for local governments. In 2019, the five real estate special taxes totaled 1.93 trillion yuan, accounting for 19% of local tax revenue. Second, land transfer fee is the most important off-budgetary revenue of local governments. Its size in 2018 was 6.5 trillion yuan, accounting for 66.5% of local fiscal revenue.
Finally, stability of the supply chain related to the real estate sector is important to employment. The long chain has created a large number of jobs. In 2018, the construction industry attracted approximately 53.6 million migrant workers, and the real estate sector has created 4.66 million positions in urban areas. Therefore the role of real estate in creating employment cannot be ignored.
V. Periodical and marginal policy easing should be applied to the real estate sector
Under the impact of the epidemic, the difficulties faced by the real estate market across the country are both unique and universal.
On the one hand, local governments should relax the restrictions on pre-sale and purchase of housing based on actual conditions so as to boost demand and reduce pressure on the capital chain of housing enterprises. On the other hand, local governments should make periodical and marginal adjustments to existing policies that restrict the financing of real estate companies during this special time, a move to stabilize the capital flow and avoid serious negative spillover effect on the economy and the financial system.
At present, macroeconomic policies released by the central government and measures adopted by local governments have reduced some pressure of the real estate industry. More than ten provinces and cities have issued relevant policies. Against this background, the following suggestions are proposed:
First, the real estate sector should have policy support like other industries, providing credit assistance to housing companies. Secondly, at regulatory level, moderately relax quotas imposed on the industry. Thirdly, reduce or exempt taxes and fees, and extend payment deadlines. Finally, encourage local governments to implement tailored policies based on the actual situations of various regions and enterprises, and offer targeted support.
References:
1. Policy Suggestions on Promoting Sound Development of the Real Estate Sector amid the Epidemic by China Real Estate Chamber of Commerce. [online]Retrieved at: http://finance.eastmoney.com/a/202002121381089217.html Feb. 12, 2020
2. Ping An Securities. Investment Strategy Report for Feb. 2020: Uncertainties Linger on the Epidemic and Easing Policy is Expected. Feb. 5, 2020
3. Finance United Press. Recent Interest Rates on International Bond Issuance Will Further Increase Risks of Debt Default. Feb. 17, 2020